Understanding Plaque Psoriasis on Lower Legs
Intro
Plaque psoriasis is more than just a skin condition; it has profound implications for those who suffer from it, especially when it impacts visible areas like the lower legs. For many, this localization not only affects physical health but also carries psychological consequences. Understanding the multifaceted nature of plaque psoriasis is essential for effective management and improved quality of life.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various aspects surrounding plaque psoriasis specifically in the context of the lower extremities. This examination will include a detailed discussion on its etiology, clinical manifestations, and possible treatment approaches. The objective is to create a nuanced understanding of this condition, leveraging the latest research and clinical insights to inform medical professionals and provide support for individuals affected by plaque psoriasis.
The discussion herein aims to weave together elements of genetic predisposition, immunological responses, and environmental triggers that may contribute to the condition. Moreover, the psychological dimensions will be addressed, as they play a significant role in shaping the overall experience of those living with plaque psoriasis. This overview sets the stage for a comprehensive investigation into one of dermatology's complex disorders.
Foreword to Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is a significant dermatological condition that warrants careful examination. This introduction aims to highlight key considerations regarding plaque psoriasis, particularly in its manifestation on the lower legs. Understanding this condition is essential, not only for those directly affected but also for healthcare professionals involved in treatment and management.
The focus on the lower legs stems from their visibility and the emotional impact that lesions can have on individuals. When lesions appear on these areas, it can exacerbate feelings of self-consciousness, leading to social withdrawal and psychological distress. Addressing these aspects is essential for comprehensive understanding and care.
Moreover, this article delves into multiple dimensions of plaque psoriasis including its pathophysiology, symptoms, and the various strategies for clinical management. Each subsection provides essential context, aiming to equip readers with a nuanced understanding that integrates current research and clinical practice. In doing so, we hope to foster better awareness and support for individuals diagnosed with this chronic condition.
Definition of Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the rapid proliferation of skin cells. This condition leads to the formation of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. These lesions typically appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower legs. The exact cause remains complex, involving a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers.
The plaques form due to an overactive immune response, which mistakenly targets healthy skin cells. This results in inflammation and accelerated skin cell turnover, leading to the distinctive lesions that are hallmarks of the disease. Understanding this definition is crucial as it lays the foundation for recognizing symptoms, triggers, and appropriate treatment methodologies.
Prevalence and Demographics
The prevalence of plaque psoriasis varies by geographic region and population group. Studies estimate that about 2-3% of the global population is affected, but the incidence can be higher in certain demographics. For example, it tends to be more common in Caucasian individuals, and there is also a notable familial correlation, pointing towards genetic predisposition.
In addition to genetic factors, lifestyle choices and underlying health conditions, such as obesity and diabetes, have been linked with increased risk. The impact of plaque psoriasis on various demographics highlights the need for tailored treatment approaches that consider both medical history and personal context.
"Plaque psoriasis affects individuals across all demographics; however, it exhibits particular prevalence patterns that underscore the need for targeted research and intervention."
To fully grasp the significance of this condition, it is imperative to comprehend both its definitions and prevalence. This understanding serves as a stepping stone into deeper discussions about etiology, clinical features, and management strategies.
Etiology of Plaque Psoriasis
The etiology of plaque psoriasis provides critical insights into the factors that contribute to the development and exacerbation of this chronic skin condition. Understanding these elements is essential for healthcare professionals and researchers, as it guides effective treatment modalities and preventive strategies. Plaque psoriasis manifests as red, scaly patches, and its underlying causes are rooted in a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and immune system responses. Given that psoriasis often impacts visible areas, like the lower legs, identifying the etiology can help in tailoring individualized care plans and manage patient expectations.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a prominent role in the onset of plaque psoriasis. Research indicates that individuals with a family history of psoriasis have a significantly higher risk of developing the condition. Specific genes, notably those in the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) complex, have been associated with increased susceptibility. These genetic determinants influence various biological pathways, including immune response and skin cell proliferation. The presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes such as IL12B and TNFAIP3 have been linked to psoriatic disease.
By understanding the genetic basis, medical professionals can enhance early diagnosis and offer targeted therapies that reflect the patient’s genetic background. Moreover, genetic counseling may provide insight for at-risk individuals, reiterating the importance of family history in risk assessment.
Environmental Triggers
While genetics lays the groundwork, environmental triggers often act as catalysts that provoke flare-ups of plaque psoriasis. Various factors contribute to this, including:
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburn can trigger a psoriatic response.
- Infections: Streptococcal infections, particularly in children, can precipitate the disease.
- Stress: Emotional and physical stress has been widely acknowledged as a significant trigger for flare-ups.
- Weather Conditions: Cold, dry weather tends to worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs, including lithium and beta-blockers, are known to exacerbate psoriasis.
Recognizing these triggers is vital for patients to manage lifestyle choices and minimize exacerbations. Patients benefit from keeping a detailed record of potential triggers to support treatment planning.
Immune Response Mechanisms
The immune system's involvement in plaque psoriasis underscores its classification as an autoimmune disorder. In this context, T cells, which are usually responsible for protecting the body against infections, mistakenly attack healthy skin cells. This autoimmune response leads to an inflammatory cascade characterized by the release of cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-17 (IL-17).
The chronic inflammation stimulates keratinocyte proliferation, resulting in the characteristic plagues of psoriasis. Studies show that targeting these immune pathways, particularly through biologic therapies that inhibit TNF-α or IL-17, can result in significant clinical improvement for many patients.


Understanding these immune mechanisms not only informs treatment strategies but also offers a window into potential future research avenues, including vaccinations or immunotherapies aimed at resetting the dysfunctional immune response.
"Addressing the etiology of plaque psoriasis allows for a comprehensive understanding that can directly influence the management strategies for affected individuals."
Clinical Manifestations on Lower Legs
Understanding the clinical manifestations of plaque psoriasis on the lower legs is essential. These manifestations not only define the physical appearance of the condition but also influence the management and treatment approach. Recognizing the specific characteristics, associated symptoms, and overall impact on the individual's quality of life is crucial for developing effective treatment plans.
Characteristics of Lesions
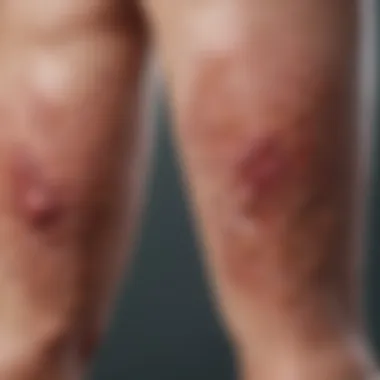
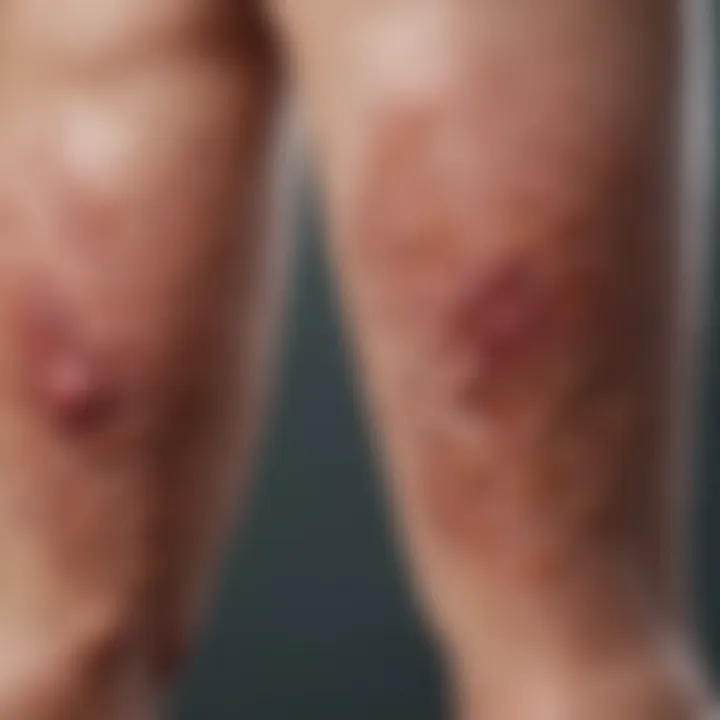
Lesions in plaque psoriasis typically present on the lower legs as well-defined, raised, and reddened patches. These lesions are often covered with silvery-white scales that can become thickened over time. The size, shape, and distribution of these plaques can vary considerably. On the lower legs, they may appear symmetrically or asymmetrically. It is common for the lesions to be prone to fissuring, particularly in areas where skin experiences friction, such as the ankles. The extent of lesion coverage can range from small patches to more extensive involvement of the skin surface.
Patients may report sensations of itching or burning, often exacerbating symptoms. The severity of these lesions may fluctuate based on various factors, including ongoing treatment, stress levels, and environmental conditions. This variability is a key consideration during clinical assessments.
Associated Symptoms
Beyond the visible lesions, plaque psoriasis on the lower legs often presents with additional symptoms. Patients may experience localized pain or tenderness, particularly when the plaques are inflamed or irritated. Other common symptoms include:
- Pruritus: This is often severe, driving patients to scratch and potentially complicating healing.
- Dry Skin: The skin may be dry and cracked in areas affected, providing further discomfort.
- Joint Pain: In more severe cases, some patients might develop psoriatic arthritis, leading to joint stiffness or swelling.
Acknowledging these associated symptoms is vital for health care providers. It can assist in forming a more comprehensive treatment strategy that addresses both the physical and psychological needs of the patient.
Impact on Quality of Life
The presence of plaque psoriasis on the lower legs can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Many patients experience self-consciousness or embarrassment related to their condition, particularly when lesions are visible during social or professional interactions. This can lead to a range of psychosocial effects, including:
- Social Withdrawal: Individuals may avoid social situations or activities, fearing judgment or misunderstandings from others.
- Decreased Self-Esteem: The persistent visibility of lesions can lead to feelings of inadequacy or discomfort in one's skin.
- Mental Health Issues: There is a higher prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic skin conditions, including plaque psoriasis.
"The consequences of plaque psoriasis extend beyond the skin. Psychological well-being is as significant as physical treatment."
Ultimately, the interplay of visible symptoms, associated discomfort, and resulting emotional strain highlights the importance of addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of managing plaque psoriasis on the lower legs. An informed approach is necessary to provide patients with holistic care that promotes improved quality of life.
Diagnosis of Plaque Psoriasis
The diagnosis of plaque psoriasis is a crucial aspect of understanding this condition. It is essential for effective management and treatment planning. Accurate diagnosis helps healthcare providers distinguish plaque psoriasis from other dermatological disorders, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate interventions. Moreover, early diagnosis can aid in minimizing the impact on quality of life, particularly for those affected by lesions on visible areas like the lower legs.
Clinical Examination
The clinical examination is the first step in diagnosing plaque psoriasis. During this examination, a healthcare professional assesses the appearance and characteristics of the skin lesions. Typical features include raised, red plaques covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques may vary in size and can appear on various parts of the body, but the lower legs often show prominent signs. The clinician will also consider accompanying symptoms such as itching or burning sensations.
The clinical examination serves as a fundamental method for identifying plaque psoriasis, enabling tailored management strategies.
In some cases, the patterns of the plaques can offer insights into the duration and severity of the condition. Patients’ medical history, including any family history of psoriasis, is also taken into account. This history can provide clues about the genetic components of the condition, which can significantly impact the diagnosis and subsequent management.
Histopathological Assessment
In certain situations, a histopathological assessment is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of plaque psoriasis. This process involves taking a small skin biopsy from a lesion and analyzing it under a microscope. The histopathological features of plaque psoriasis include the presence of hyperkeratosis, which is the thickening of the outer layer of skin, and an increased number of inflammatory cells. These findings are consistent with the immune dysregulation seen in psoriasis.
Histopathological assessment can be particularly beneficial in complex cases where the clinical presentation is ambiguous or where other skin conditions might resemble psoriasis. Results from the biopsy contribute significant information that can guide treatment decisions and the understanding of the disease's severity.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is another critical component in the diagnosis of plaque psoriasis. Several skin conditions present with similar features, making it essential to differentiate between them. These conditions may include eczema, contact dermatitis, and fungal infections, among others. Each of these conditions requires distinct treatment approaches.
The comprehensive evaluation during the diagnosis often includes a review of symptoms and physical examination findings in relation to these other skin disorders. Dermoscopy, a non-invasive technique for examining skin lesions, can also be employed to facilitate accurate diagnosis. Engaging in differential diagnosis helps in avoiding mismanagement and ensures that patients receive the right treatments that suit their specific conditions.
Management Strategies
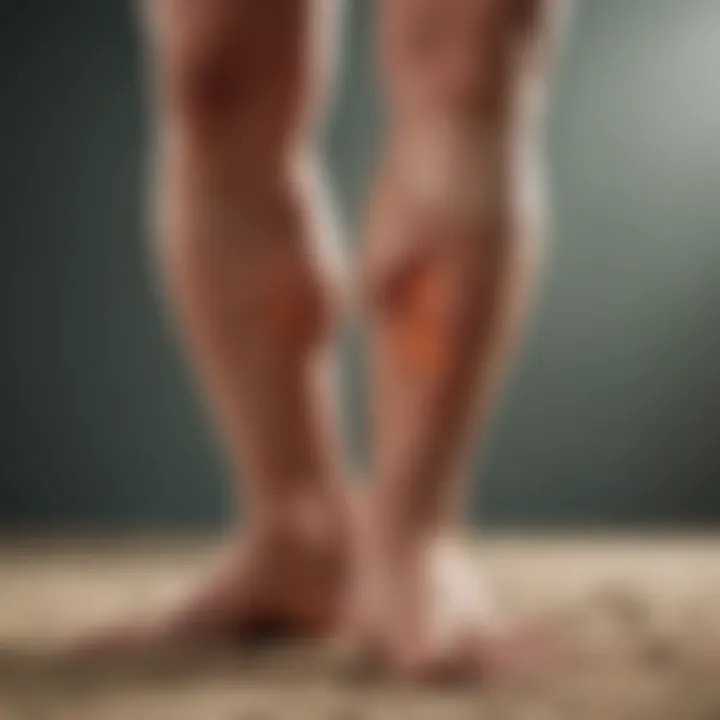


Effective management strategies for plaque psoriasis, particularly when it affects the lower legs, are crucial in improving the quality of life for individuals. The treatment options can be diverse and might include both topical and systemic approaches. Recognizing the significance of these strategies leads to better compliance and health outcomes. Patients should understand the potential benefits and limitations of each method, to make informed decisions regarding their treatment.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against plaque psoriasis. These are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce lesions and alleviate symptoms. Three notable categories within this treatment modality are steroid creams, vitamin D analogues, and emollients.
Steroid Creams
Steroid creams are a common choice for the management of plaque psoriasis due to their powerful anti-inflammatory properties. They reduce redness, itching, and swelling effectively. One key characteristic of steroid creams is their ability to penetrate the skin layers, delivering relief to the affected area rapidly. Because of their effectiveness, many clinicians often prescribe this option as a first-line treatment for localized lesions. However, while they can provide immediate relief, prolonged use may lead to skin thinning or other side effects, which clinicians must consider when creating a treatment plan.
Vitamin Analogues
Vitamin D analogues, such as calcipotriene, play a crucial role in managing plaque psoriasis. They help regulate skin cell growth, a vital aspect since psoriasis is characterized by rapid cell proliferation. One of the key characteristics of vitamin D analogues is their potency; they can be as effective as steroid creams without the side effects associated with long-term steroid use. Despite their benefits, patients may experience irritation or a burning sensation upon initial application. Therefore, gradual introduction into the treatment regimen is advisable for better tolerance.
Emollients
Emollients serve a distinct but equally important function in the management of plaque psoriasis, particularly for maintaining skin hydration. They help soothe the skin, reduce dryness, and provide a barrier against environmental irritants. A key aspect of emollients is their ability to enhance the effectiveness of other topical treatments by improving skin permeability. While they are beneficial for all skin types, individuals may require different formulations based on their specific skin concerns. Regular use of emollients might prevent flare-ups and keep the skin optimal for healing.
Systemic Treatments
When topical treatment proves insufficient, systemic treatments may be the next step. These treatments affect the entire body and are usually prescribed for moderate to severe cases of plaque psoriasis. Two main categories are oral medications and biologic therapies.
Oral Medications
Oral medications such as methotrexate or acitretin are potent options available for managing severe plaque psoriasis. The key characteristic of these medications is their systemic action, providing broad relief from lesions. They often decrease skin cell turnover and reduce inflammation throughout the body. However, the potential for side effects, such as liver damage or teratogenic risks, is significant, necessitating regular monitoring by healthcare providers.
Biologic Therapies
Biologic therapies represent a more targeted approach to treating plaque psoriasis. Medications like adalimumab or etanercept are designed to inhibit specific pathways involved in the immune response. They hold a prominent place due to their efficacy and potential long-lasting benefits. A distinctive feature is their route of administration, often through injection or infusion, which may require visits to specialized clinics. Patients might find these therapies advantageous due to their ability to achieve dramatic improvements. However, accessibility and high costs are barriers that can affect their widespread use.
Phototherapy Options
Phototherapy options, including ultraviolet light treatment, also play an essential role in managing plaque psoriasis. This method objectively targets lesions and can lead to significant improvement. Controlled exposure to specific wavelengths of light has been found effective in reducing redness and scaling. However, individuals undergoing phototherapy must be monitored for skin damage to avoid adverse effects such as increased risk of skin cancer.
Important Note: Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or changing any psoriasis treatment regimen.
By understanding these management strategies, individuals can make informed choices about their treatment and potentially reduce the burden of plaque psoriasis on their daily lives.
Psychosocial Considerations
Plaque psoriasis is not only a matter of skin health; it profoundly affects the psychosocial well-being of individuals. Recognizing the psychosocial implications is crucial in understanding the comprehensive experience of living with this skin condition. The emotional distress often stems from visible symptoms. The discomfort and changes in skin appearance can lead to feelings of embarrassment and shame. Therefore, the psychosocial considerations surrounding plaque psoriasis warrant a focused exploration.
Mental Health Implications
Mental health issues frequently co-occur with plaque psoriasis. The ongoing management of physical symptoms can contribute to increased levels of anxiety and depression. Various studies show that individuals with psoriasis are at a higher risk of experiencing mood disorders compared to the general population.
Some specific mental health implications include:
- Low self-esteem: Many people with plaque psoriasis often face challenges regarding their body image, leading to diminished self-worth.
- Emotional distress: The unpredictability of flare-ups can create anxiety about when and where lesions may reappear.
- Social withdrawal: To avoid potential embarrassment, some individuals might isolate themselves from social situations, leading to loneliness.
"Mental health is as important as physical health. Addressing psychological needs is vital for improving outcomes in individuals with plaque psoriasis."
Social Stigma and Discrimination
Social stigma surrounding psoriasis often adds another layer of complexity to the lives of affected individuals. This stigma can manifest in various ways, from teasing to discrimination in social or professional environments. The visible nature of plaque psoriasis makes it a target for judgment and negative assumptions.
Key aspects of this stigma include:


- Misunderstanding of the condition: Many people are unaware that psoriasis is not contagious, leading to misconceptions about risk of transmission.
- Peer reactions: Some individuals report feeling alienated due to the reactions of others who may express discomfort around them.
- Impact on employment: In some cases, individuals with visible psoriasis may face discrimination in hiring processes or promotions, affecting their career opportunities.
Understanding these psychosocial dimensions is essential. It enables both medical professionals and the individuals affected to address not only the physical but also the emotional needs in treatment plans. Integrating mental health support into dermatological care can improve the overall quality of life for those living with plaque psoriasis.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing plaque psoriasis, particularly when it affects visible areas such as the lower legs. By making informed choices regarding diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle habits, individuals can help reduce the severity of their symptoms and improve their quality of life. This section delves into two primary aspects: diet and nutrition, as well as exercise and physical activity, further emphasizing their significance in the holistic management of plaque psoriasis.
Diet and Nutrition
The connection between diet and skin health is well-documented. Certain foods may contribute to inflammatory processes that exacerbate plaque psoriasis. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory elements can mitigate flare-ups. Here are some dietary considerations for those with plaque psoriasis:
- Include Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Consuming fish like salmon or sardines may be beneficial. Omega-3 fatty acids are known to have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Increase Intake of Fruits and Vegetables: A diverse array of fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants, which are essential for combating oxidative stress in the body.
- Limit Processed Foods: Highly processed and sugary foods can contribute to inflammation. Reducing refined sugars and saturated fats is advisable.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking sufficient water supports overall skin health and aids in toxin elimination.
Making dietary changes can be challenging, but it is important to be patient and persistent. Each person's response to food varies, so keeping a food diary might help in identifying triggers. Consider working with a nutritionist who understands plaque psoriasis to create a tailored meal plan.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is vital not only for physical health but also for mental well-being. For individuals with plaque psoriasis, exercise can help in multiple ways:
- Stress Reduction: Physical activity is a well-known stress reliever. Lowering stress may lead to fewer psoriasis flare-ups.
- Weight Management: Excess weight can worsen symptoms and affect treatment efficacy. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential.
- Improved Circulation: Regular movement enhances blood flow, which may support skin healing.
Engaging in activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can be particularly beneficial. It's crucial to choose exercises that feel enjoyable and sustainable. Individuals should discuss with their doctors any specific exercise plans, especially if they are experiencing joint pain associated with psoriatic arthritis.
Remember: Lifestyle modifications are not a substitute for medical treatment but can significantly enhance overall management of plaque psoriasis.
In summary, deciding to modify one’s lifestyle is a proactive step toward controlling plaque psoriasis. The combined approach of dietary adjustments and increased physical activity can foster an environment that is less conducive to flare-ups, ultimately leading to improved well-being.
Research Advances
Research advances in plaque psoriasis are crucial for enhancing our understanding of this complex skin condition, especially when it affects visible areas such as the lower legs. The investigation of new therapeutics and genetic factors plays a significant role in developing effective treatments and improving patient outcomes. By focusing on emerging therapies and advancements in genetic research, we can better address the needs of those affected.
Emerging Therapeutics
Emerging therapeutics represent a vital area of focus in the treatment of plaque psoriasis. These new treatment options often aim to target specific pathways involved in the disease's pathophysiology. Recent research has explored medications that modulate the immune system more precisely than traditional therapies.
- Biologic agents have gained prominence due to their ability to target specific immune responses. Drugs like ustekinumab and secukinumab focus on interleukins that fuel inflammation, leading to poignant improvement in plaque psoriasis symptoms.
- Another promising area is small molecules, which can be taken orally and may offer ease of use. These compounds can inhibit specific enzymes associated with psoriasis progression.
- Topical therapies are also evolving, with advanced formulations designed to enhance absorption and minimize side effects.
Understanding these emerging options allows clinicians to personalize treatment, focusing on efficacy and safety. It is essential to stay abreast of ongoing clinical trials to evaluate the long-term impacts of these therapies on patients.
Genetic Research Developments
Genetic research developments have opened new avenues in understanding plaque psoriasis. The condition has a strong hereditary component, and recent studies have identified several genetic loci associated with its onset and severity.
- Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have pinpointed variants in genes related to immune functions, particularly those involved in inflammatory responses. This information can help in predicting susceptibility to psoriasis.
- Understanding genetic predispositions allows researchers to explore precision medicine, where treatments can be tailored based on an individual's genetic profile.
- New findings regarding the epigenetic factors that might influence gene expression offer additional insights. These developments could lead to novel therapeutic strategies that target the underlying paths of disease.
The integration of genetic and therapeutic research holds great promise for transforming approaches to managing plaque psoriasis.
Culmination
The conclusion of an article on plaque psoriasis, especially focusing on the lower legs, is pivotal not only as a recap but alsso as a guide for future considerations in the field. This section encapsulates the essential findings and observations throughout the article while emphasizing the broader implications for those affected by the condition.
An effective conclusion highlights the complexity of plaque psoriasis, underscoring that it is not merely a skin disease but a multifaceted condition that influences various aspects of patients' lives. It urges the importance of individualized treatment plans that take into account the diverse factors contributing to the disease’s manifestation.
Summary of Key Points
- Definition and Prevalence: Understanding plaque psoriasis involves recognizing its definition as a chronic autoimmune condition, with rising prevalence in various demographics.
- Etiological Factors: A blend of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers plays a critical role in pathogenesis.
- Clinical Features: Lesions on the lower legs are a source of discomfort and embarrassment, impacting the quality of life significantly.
- Diagnosis Methods: Clinical examinations, histopathology, and differentiating from similar conditions form the basis for accurate diagnosis.
- Management Strategies: Treatments ranging from topical steroids to systemic biologics provide various options, suited to individual patient needs. Lifestyle modifications also have a significant impact on managing the disease.
- Psychosocial Impact: Mental health issues and social stigma often accompany visible skin conditions. Acknowledging this aspect is crucial for holistic management.
- Ongoing Research: Emerging therapies and genetic studies offer promising avenues for future treatment strategies.
Future Directions in Research
Research into plaque psoriasis continues to evolve, with several key areas identified for further exploration:
- Genetic Research Developments: Investigating specific genetic markers could lead to improved diagnostics and targeted therapies.
- Psychological Studies: More comprehensive studies on the mental health aspects of plaque psoriasis can inform treatment approaches that incorporate psychological support.
- Innovations in Treatment: The development of biologic medications targeting specific pathways offers hope for more effective and personalized treatments.
- Long-term Health Implications: Understanding how plaque psoriasis affects overall health beyond the skin leads to better comprehensive care approaches.
- Environmental Factors: Researching the impact of lifestyle, diet, and environmental factors in the disease process can guide preventive strategies.







