Diagnosis of Follicular Lymphoma: An In-Depth Exploration


Article Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Follicular lymphoma is one of the more common types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that presents unique challenges for diagnosis. The importance of a precise diagnosis cannot be overstated, as it heavily influences treatment options and patient outcomes. This exploration reveals that diagnosis hinges on multiple approaches, combining clinical assessment, imaging, histopathological evaluation, and sophisticated molecular studies. Together, these methods enhance the accuracy of identifying the disease, which is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.
Research Objectives
The aim of this article is to provide a thorough review of the diagnostic processes involved in identifying follicular lymphoma. This includes:
- Understanding the role of clinical evaluations and symptoms that may point to the condition.
- Exploring imaging techniques, such as PET scans and CT scans, that aid in visualization and staging of the disease.
- Discussing the significance of histopathological examination, including biopsy workups.
- Highlighting advancements in molecular diagnostics that can further refine the accuracy of diagnoses.
- Recognizing the collaborative efforts of multidisciplinary teams to enhance diagnostic efficacy.
Key Results and Discussions
Main Findings
An amalgamation of clinical insights and technological advancements forms the heart of follicular lymphoma diagnosis. For instance, clinical evaluation often uncovers symptoms such as painless lymphadenopathy, which only adds a layer to complementary imaging findings. Imaging methods, like positron emission tomography (PET), not only visualize lesions but also provide metabolic information, which can be telling in determining the aggressiveness of the lymphoma.
Histopathological examination is critical, with biopsy samples being scrutinized for specific markers like CD10, BCL2, and BCL6. These markers are key in confirming the diagnosis and further stratifying the risk category of the lymphoma. Moreover, emerging molecular technologies, such as next-generation sequencing, have begun to play an integral role, allowing for detailed genetic profiling that paves the way for targeted therapy.
Implications of Findings
The findings underscore a multi-faceted approach to diagnosing follicular lymphoma, suggesting that relying solely on conventional methods may fall short of providing a well-rounded understanding of a patient’s condition. The integration of various diagnostic modalities not only enriches our understanding but also fine-tunes the treatment landscape, promising a more personalized approach. Furthermore, collaborations among oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists become vital, as they bring different lenses of expertise to a shared goal of accurate diagnosis.
"A precise diagnosis is the bedrock upon which effective treatment is built. Neglecting any aspect of the diagnostic puzzle is not an option."
End
In the evolving landscape of follicular lymphoma diagnosis, the significance transcends beyond mere identification. It shapes treatment modalities, informs prognoses, and ultimately affects survival rates. This exploration delves into the intricacies of diagnosis, aligning knowledge with clinical practice for optimal patient outcomes.
Intro to Follicular Lymphoma
In the realm of oncology, understanding follicular lymphoma is crucial due to its nature as one of the more commonly diagnosed subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This section dives into the fundamentals, shedding light on why a well-rounded examination of this lymphoma is essential. By grasping the intricacies of its diagnosis, healthcare professionals can tailor their treatment strategies to optimize patient outcomes.
Overview of Lymphomas
Lymphomas are a broad category of blood cancers that originate in the lymphatic system, an integral part of the body’s immune system. They can be chiefly divided into two categories: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas, which include follicular lymphoma, exhibit a variety of characteristics and behaviors based on their subtype.
Lymphomas can arise from lymphoid tissue—this can include lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow—affecting how they present and progress. Follicular lymphoma stands out due to its specific histological markers and clinical behavior. Because of its tendency to have an indolent course, recognizing its early signs is vital for timely intervention. For those interested in digging deeper, the lymphatic system’s complex functioning and the variations within lymphomas warrant further study.
- Key Points:
- Lymphomas arise from lymphoid tissues.
- Understanding different subtypes is essential for effective treatment.
- Follicular lymphoma exhibits distinct characteristics compared to other lymphomas.
Characteristics of Follicular Lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma is defined predominantly by its growth pattern. It is characterized by follicle-like structures visible under a microscope, indicating the proliferation of B-lymphocytes. This lymphoma can often be nicknamed “slow-growing,” highlighting its tendency to be asymptomatic in the early stages, leading to diagnostic challenges.
From a clinical perspective, follicular lymphoma typically manifests in the form of painless lymphadenopathy. Patients might notice swollen lymph nodes but may not immediately connect these symptoms to a potential malignancy. The heterogeneous nature of this lymphoma means that each case can be quite different. Some individuals may experience a more aggressive form, whereas others have a course that might not require immediate treatment.
"Understanding the characteristics of follicular lymphoma enlightens the way we approach diagnosis and treatment."
- Important Considerations:
- Indolent Nature: Many patients may have a prolonged asymptomatic period.
- Variable Aggressiveness: Each case can exhibit unique behaviors, necessitating tailored treatment approaches.
- Microscopic Features: Identification of characteristic follicle-like patterns in tissue samples plays a critical role in diagnosis.
In summary, delving into the characteristics of follicular lymphoma helps underline the necessity for meticulous diagnostic practices that incorporate a diversity of methodologies. As we transition into sections addressing clinical assessment and laboratory investigations, these foundational understandings will provide a necessary backdrop for comprehending the overall diagnostic narrative.
Initial Clinical Assessment
The concept of initial clinical assessment lays the groundwork for diagnosing any illness, particularly follicular lymphoma. It serves as the first line of inquiry, allowing healthcare professionals to gather essential information about the patient. This process is significantly beneficial, as it can guide subsequent diagnostic steps. Emphasizing symptom evaluation and physical examination findings, this section reveals how the initial clinical assessment can illuminate the path toward an accurate diagnosis.
Symptomatology
When it comes to follicular lymphoma, identifying the symptoms is like piecing together a puzzle. Patients often present with a myriad of manifestations that can easily be confused with benign conditions. Typical symptoms may include:
- Painless lymphadenopathy: Patients typically notice swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck, armpits, or groin. These swellings often come and go, which can allow the lymphoma to secretly propagate.
- Unexplained weight loss: A significant reduction in weight without trying is another hallmark symptom, often raising red flags.
- Fever or night sweats: These systemic symptoms can lead to a general sense of malaise or fatigue, making it hard to pinpoint the cause.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is common, affecting the quality of life and daily routines for those impacted.
Patients may not readily connect these symptoms to follicular lymphoma due to their vague and intermittent nature. As such, an astute clinician must take a comprehensive patient history, probing deeper into their experiences. Detailed inquiry helps unravel the complexity of individual symptoms and can direct suspicion toward a lymphatic malignancy.
Physical Examination Findings
Once symptomatology has been assessed, a careful physical examination follows. This is crucial, as the physical examination provides tangible evidence that can validate the initial concerns. During the examination, a physician often looks for:
- Lymph node enlargement: Palpable lymph nodes are checked for size, mobility, and consistency. Enlarged nodes may indicate active lymphatic involvement.
- Splenomegaly: The spleen might be larger in lymphoma cases, and a thorough examination can detect this abnormality.
- Examine other systems: Observing for signs of bone marrow involvement, such as pallor or bruising, can yield essential insights.
Blockquote: "The physical examination is a critical piece of the diagnostic puzzle. Without careful palpation and assessment, many cases of follicular lymphoma could be missed entirely."
In this exploratory phase, a clinician's intuition plays a vital role. Their ability to connect the dots between physical findings and patient history cannot be underestimated.


Together, symptomatology and physical examination lay the bedrock for further investigations. These elements highlight the need for diligence in the initial clinical assessment, acting as a compass for navigating the complexity of diagnosing follicular lymphoma.
Laboratory Investigations
Diagnosing follicular lymphoma relies heavily on comprehensive laboratory investigations. These tests are essential in facilitating prompt and accurate identification of the disease, ultimately guiding treatment strategies. When it comes to accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests unravel a wealth of information, aiding clinicians in understanding not only the presence of lymphoma but also its aggressiveness and potential complications. This section highlights the main components of laboratory investigations pertinent to follicular lymphoma, laying a solid groundwork for subsequent evaluations and interventions.
Blood Tests
Blood tests stand as the frontline of laboratory diagnostics for follicular lymphoma. These tests are usually among the first steps in evaluating a patient suspected of having lymphoma. Significant factors include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC provides crucial insights into the patient's overall health. It helps detect issues like anemia which may point to systemic disease.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Levels: Elevated LDH can be an indicator of tumor burden. Higher LDH levels often suggest a more aggressive disease course, which necessitates careful consideration in treatment planning.
- Immunophenotyping: This test helps identify the specific type of lymphoma based on the unique markers expressed on the surface of the lymphoma cells. For follicular lymphoma, the identification of the CD10 and BCL2 markers can be particularly telling.
"Blood tests can be as revealing as a neatly found locked diary; they unveil vital insights that guide clinical paths."
Furthermore, routine biochemical panels help assess hepatic and renal function, ensuring that patients can tolerate potential therapies. However, it’s important to note that while blood tests are invaluable, their results alone cannot definitively diagnose follicular lymphoma, making additional evaluation critical.
Bone Marrow Biopsy
The bone marrow biopsy plays a pivotal role in the diagnostic process, especially when confirming the presence of follicular lymphoma. This procedure involves taking a small sample of bone marrow, usually from the hipbone. The significance of this biopsy includes:
- Assessment of Bone Marrow Infiltration: Follicular lymphoma frequently involves bone marrow, and it is critical to understand the extent of this infiltration. Detection in the bone marrow can suggest a more advanced disease stage.
- Cellularity Evaluation: The biopsy enables the evaluation of bone marrow cellularity, helping determine if the marrow is hypercellular or hypocellular, and assessing the types of cells present.
- Cytogenetic Studies: Alongside histological assessments, these studies can indicate specific chromosomal abnormalities associated with follicular lymphoma, providing deeper insights into prognosis and tailored therapy.
Performing a bone marrow biopsy is generally safe, but it can carry risks such as infection or bleeding. Patience and preparation are integral, as the procedure can leave patients understandably anxious about potential discomfort. To streamline the process, healthcare providers often explain the procedure thoroughly, demystifying what to expect while alleviating concerns.
In summary, laboratory investigations are indispensable to the diagnosis and characterization of follicular lymphoma. Blood tests and bone marrow biopsies serve different yet complementary roles, equipping healthcare teams with the information necessary for comprehensive patient management.
Imaging Techniques for Diagnosis
Imaging techniques hold a pivotal role in the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma, acting as essential tools that guide healthcare professionals in visualizing and understanding the extent of the disease. By employing various scanning methods, clinicians are able to gather critical insights into the lymphoma's characteristics, including its location, size, and potential involvement of other organs. These imaging modalities serve to complement clinical assessments and laboratory investigations, ultimately enhancing the diagnostic accuracy.
The primary benefits of imaging include
- Detailed Visualization: Imaging provides a clear view of lymph nodes and other involved tissues, making it easier to discern patterns that might indicate malignancy.
- Disease Staging: Techniques such as CT and PET scans assist in evaluating the stage of the disease, which is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment strategy.
- Monitoring Treatment Response: Post-treatment scans are instrumental in assessing how well the lymphoma is responding to therapy, offering guidance on the next steps in management.
However, while these imaging techniques are invaluable, healthcare providers must also consider the potential limitations. Factors such as radiation exposure, cost, and accessibility can vary, which may impact patient care. The detailed exploration of three key imaging modalities follows, highlighting their roles and significance.
Role of Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are a cornerstone in the diagnostic process for follicular lymphoma. They provide cross-sectional depictions of the body, allowing for an insightful visualization of lymph node architecture.
Why CT Scans Matter:
CT imaging is particularly useful because:
- Comprehensive View: It captures detailed images of both the lymphatic system and surrounding structures, facilitating the detection of enlarged lymph nodes.
- Staging Benefits: The ability to identify spread to other organs is crucial for staging and treatment planning.
In practice, CT scans help healthcare professionals distinguish between benign and malignant lymphadenopathy. However, it’s important to combine CT findings with other diagnostic methods as not all abnormalities detected on CT translate to lymphoma.
Position Emission Tomography (PET) Scans
Position Emission Tomography (PET) scans add another layer to the diagnostic arsenal, offering insights into the metabolic activity of lymphoma cells. This method provides information that is not accessible through CT alone, enhancing the overall diagnostic picture.
Significant Aspects of PET Scans:
- Metabolic Insights: PET scans utilize radiotracers that reveal the metabolic activity of tissue, pinpointing areas of increased activity typical of lymphomas.
- Treatment Evaluation: These scans can be used to monitor treatment efficacy, particularly in detecting early responses to therapy.
PET scans are often paired with CT scans; the fusion of these two imaging techniques—referred to as PET/CT—provides a more integrated diagnostic view, combining anatomical detail with metabolic function.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is another imaging modality that is gaining traction in the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma, particularly in certain contexts where other methods may not suffice.
Importance of MRI in Diagnostics:
- Soft Tissue Contrast: MRI excels in providing clear images of soft tissues, making it particularly useful for evaluating lymph nodes in challenging anatomical locations, such as the mediastinum or abdomen.
- No Radiation: Unlike CT and PET scans, MRI does not expose patients to ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for ongoing monitoring.
Nonetheless, MRI may not be as widely available and can be more expensive than CT. Its role often tends to be supplementary, used when a clearer detail of soft tissue structures is necessary or when evaluating complications.
In summary: Imaging techniques like CT, PET, and MRI are indispensable for diagnosing and staging follicular lymphoma. Each modality offers unique insights that, when combined, provide a comprehensive understanding of the disease's landscape.
Histopathological Diagnosis
In the realm of diagnosing follicular lymphoma, histopathological diagnosis stands as a cornerstone. This approach is essential since it provides defined characteristics of the lymphoma at a cellular level. The diagnostic process isn’t just about identifying cancer; it’s about pinpointing the specific type and stage to ensure that patients receive the best possible care tailored to their individual circumstances. Histopathology enables oncologists to delineate between benign conditions and aggressive lymphomas, which can significantly alter treatment decisions.
The significance of histopathological diagnosis can be summarized through a few key elements:
- Cellular Analysis: It allows for the identification of atypical lymphoid cells that are hallmark features of follicular lymphoma. Pathologists scrutinize tissue samples under microscopes to reveal cellular structures that may indicate malignancy.
- Grading and Subtyping: Histopathological examination helps in determining the grade of lymphoma, guiding treatment options. Knowing whether it is low-grade or high-grade can influence prognosis and therapeutic strategies.
- Tumor Microenvironment: It sheds light on the microenvironment in which the cancer exists, understanding factors that may contribute to tumor behavior and growth patterns.
"An accurate histopathological diagnosis can be the difference between effective treatment and a potentially dangerous oversight."
Importance of Biopsy
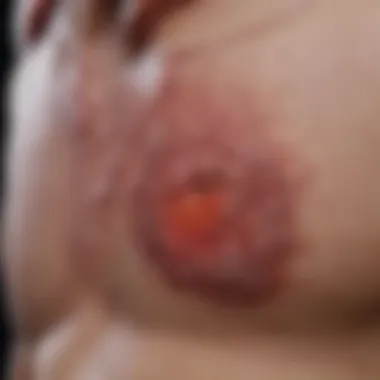

A biopsy is paramount in the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma. This method involves taking a small sample of the affected tissue for examination. The accuracy of the biopsy directly influences patient outcomes. Here are several key points regarding the importance of biopsy in diagnosing this form of lymphoma:
- Definitive Diagnosis: Without biopsy, clinicians work in a foggy realm of possibilities. The information gathered from a biopsy provides a solid foundation for a diagnosis, ensuring that treatment is initiated based on concrete data.
- Choice of Treatment: Identifying specific subtypes of lymphoma through biopsy informs oncologists about the most effective treatment options.
- Risk Assessment: A biopsy can also evaluate the spread of the disease. Understanding the extent of the lymphoma assists in staging the disease and determining the urgency of intervention.
Microscopic Examination Techniques
The microscopic examination of biopsy samples reveals a treasure trove of information crucial for diagnosing follicular lymphoma. Techniques employed vary, but they share a common goal: revealing minuscule details about the cellular architecture and behavior. Some prevalent techniques include:
- Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining: This standard staining technique helps highlight different structures within the tissue, allowing pathologists to assess cell morphology effectively. It’s often the first step in understanding the nature of the sample.
- Immunohistochemistry: This technique utilizes antibodies to detect specific antigens on cells. In follicular lymphoma, identifying markers such as CD10, BCL2, and others provide critical insight into the lymphoma subtype and its differentiation from other types of lymphoproliferative disorders.
- Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH): FISH is a technique that uses fluorescent probes to identify genetic abnormalities within the cells. It plays a significant role in detecting chromosomal translocations that are characteristic of follicular lymphoma, such as the t(14;18) translocation.
With the combination of these techniques, pathologists can glean a comprehensive picture of the lymphoma’s characteristics, ultimately aiding in delivering precise and tailored patient management.
Molecular Diagnostics
Molecular diagnostics play a pivotal role in diagnosing follicular lymphoma, significantly enhancing the accuracy and efficacy of the diagnostic process. This encompassing approach allows for a nuanced understanding of the genetic underpinnings of this condition, providing insights that traditional methods may overlook. The adoption of molecular techniques in oncology not only improves our ability to pinpoint follicular lymphoma but also aids in tailoring treatment plans for individual patients, underscoring the prospect of personalized medicine.
One of the substantial benefits of incorporating molecular diagnostics is the possibility of detecting specific genetic alterations that drive the disease. With follicular lymphoma, hallmark genetic changes, like the t(14;18) translocation, serve as essential markers for diagnosis and prognosis. Identifying these alterations can help in confirming a suspected diagnosis and possibly lead to earlier intervention. Moreover, this approach has implications for monitoring treatment response and disease progression, as persistent or evolving mutations can indicate a relapse or refractory disease.
However, the integration of molecular diagnostics also comes with its own set of considerations. Variability in testing protocols, costs, and access to advanced technology can create barriers for some patients. Moreover, the interpretation of molecular test results requires a high level of expertise to ensure that findings are contextually weighed against clinical data, minimizing the risk of misguidance.
"Molecular diagnostics not only shines a light on the genetic landscape of follicular lymphoma but also opens avenues for innovative therapies and personalized treatment plans."
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing has emerged as a cornerstone of molecular diagnostics in follicular lymphoma. This process typically involves screening for specific gene mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, and patterns of gene expression. The identification of the BCL2 gene rearrangements, often associated with follicular lymphoma, is one of the most classic examples. Such information can provide oncologists with critical insights regarding the biological behavior of the disease and the likelihood of an aggressive course.
In clinical practice, genetic testing can also address the question of familial predisposition, as lymphomas can be influenced by inherited genetic factors. Understanding these inherited risks can assist in surveillance and early intervention strategies for high-risk individuals, increasing the potential for favorable outcomes.
However, genetic testing is not without its challenges. Discussions surrounding the implications of test results can be complex, especially concerning potential psychological impacts on patients and their families. Hence, genetic counseling becomes an integral part of the testing process, ensuring that patients are equipped with the knowledge and support they need to navigate their results.
Next-Generation Sequencing
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) marks a seminal advancement in the field of molecular diagnostics, offering comprehensive insights into the genetic landscape of follicular lymphoma. Unlike traditional methods, which often focus on single gene analysis, NGS allows for the simultaneous evaluation of multiple genes, providing a broader view of the genetic alterations present within the cancer.
This technology enhances our ability to uncover novel mutations and variants that may contribute to tumor development and resistance to therapy. For instance, the assessment of the whole exome can reveal mutations in genes involved in key pathways of cell death and proliferation—information that holds the promise of guiding therapy decisions. Consequently, NGS facilitates not just diagnosis but also the selection of targeted therapies that may lead to better outcomes.
Despite its potential, the implementation of NGS poses some challenges. The volume of data generated can be overwhelming, requiring sophisticated analytical platforms and expertise. Moreover, there is a need for ongoing studies to validate the clinical relevance of certain mutations, guiding the development of more effective targeted treatments.
In summary, the rise of molecular diagnostics, specifically through genetic testing and next-generation sequencing, presents a transformative shift in the diagnosis and management of follicular lymphoma, bringing a new level of precision that is essential for optimizing patient care.
Staging of Follicular Lymphoma
Staging is a critical component in understanding and managing follicular lymphoma. It establishes the breadth of the disease, providing valuable insights into how far the lymphoma has spread and guiding therapeutic choices. The staging process takes various factors into account, including the number of affected lymph nodes, the presence of extranodal involvement, and specific biological characteristics of the lymphoma itself.
Importance of Staging
Staging not only informs the treatment plan but also helps in predicting the prognosis for patients. It can dictate whether a patient may need immediate treatment or if they can be monitored safely. Moreover, accurate staging can enhance communication among healthcare providers, paving the path for a more coordinated approach to patient care.
"A well-staged lymphoma lays the groundwork for a targeted treatment strategy, aiming to improve patient outcomes and minimize unnecessary interventions."
Such benefits underscore why accuracy in staging is paramount. Understanding each patient's stage can impact clinical trials, enrollment criteria, and ultimately reshape approaches to therapy. Thus, it's not merely a bureaucratic step; staging can indeed be a lifeline.
Ann Arbor Staging System
The Ann Arbor Staging System is one of the most widely used frameworks for categorizing lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma. It includes four stages, each with specific features:
- Stage I: Involvement of a single lymph node region or a single extranodal site.
- Stage II: Involvement of two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm.
- Stage III: Involvement of lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm, which may also include the spleen.
- Stage IV: Disseminated involvement of one or more extranodal sites, with or without lymph node involvement.
This classification system assists in shaping treatment decisions. For instance, patients in earlier stages may be candidates for localized therapy, while advanced stages might necessitate more intensive systemic therapy.
Role of International Prognostic Index
The International Prognostic Index (IPI) is often used alongside the Ann Arbor system to provide a more nuanced outlook on patient prognosis and therapy. It considers factors such as:
- Age
- Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels
- Performance status
- Number of extranodal sites
- Presence of stage IV disease
By combining information from both the IPI and the Ann Arbor Staging System, healthcare professionals can develop a comprehensive view that not only determines treatment plans but also estimates survival probabilities for their patients. This holistic approach minimizes one-size-fits-all treatment plans and fosters a more personalized treatment journey.
Understanding these staging systems can be instrumental in the multifaceted approach to diagnosing and managing follicular lymphoma, ensuring that patients receive the right interventions at the right time.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Diagnosing follicular lymphoma is no walk in the park. It’s a complex process that often presents obstacles that can impact patient outcomes significantly. Understanding these challenges is crucial for clinicians, educators, and anyone invested in cancer research or treatment. This section delves into two primary areas of concern: diagnostic delays and misdiagnosis risks. Each element plays a pivotal role in the overall accuracy and timeliness of the diagnosis.
Diagnostic Delays
When it comes to diagnosing follicular lymphoma, timing can feel like a waiting game, with stakes that run high. Diagnostic delays can be frustrating and lead to unnecessary extended periods of uncertainty for patients and their families. Several factors contribute to these delays:
- Patient Presentation: Patients may not exhibit overt symptoms initially, leading to missed appointments or dismissed concerns.
- Healthcare System Flaws: Sometimes, there are bottlenecks in the healthcare system itself. Long wait times for appointments and tests can stall the diagnostic progress.
- Limited Awareness: There is often a lack of awareness among primary care physicians regarding the subtle symptoms associated with follicular lymphoma, which can delay a referral to a specialist.

A study indicated that prolonged diagnostic processes can lead to poorer outcomes, as more advanced stages of the disease are harder to treat. Patients might find themselves coping with anxiety, frustration, and a sense of helplessness, all while waiting for definitive answers.
"Timely diagnosis is paramount; it not only affects treatment options but also impacts prognostic outcomes for follicular lymphoma patients."
In light of these challenges, improving the speed and accuracy of diagnosis can be transformed through:
- Enhanced Training: Educating primary care providers about the red flags associated with follicular lymphoma.
- Streamlined Referral Processes: Enhancing communication among care providers to expedite referrals.
- Proactive Patient Engagement: Encouraging patients to advocate for themselves and facilitate timely discussions about their health concerns.
Misdiagnosis Risks
Alongside delays, the risks of misdiagnosis pose a serious threat in the clinical setting. It’s not just the initial diagnostics that matter; the accuracy of those conclusions greatly influences the path forward. Misdiagnosis can stem from various factors:
- Symptom Overlap: Follicular lymphoma shares symptoms with other conditions, complicating the diagnostic landscape. Fatigue, weight loss, and night sweats can be attributed to numerous ailments, which can lead to confusion and misinterpretation.
- Histological Challenges: The histopathological landscape is fraught with complexity. Follicular lymphoma may exhibit variable histological features that complicate microscopic assessment. Misinterpretation might emerge from a lack of experience or subtlety in distinguishing between lymphoma and benign conditions.
- Integration of Molecular Technologies: As molecular diagnostics become more common, the misunderstanding of genetic markers can lead to miscategorization of the lymphoma type. This is especially pivotal given the impact that specific treatments can have on differing lymphoma subtypes.
Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatments, which might worsen patient conditions instead of improving them. The repercussions extend beyond the individual, burdening both healthcare systems and families economically and emotionally.
To mitigate these risks, healthcare teams can adopt approaches such as:
- Collaborative Diagnosis: Engaging multidisciplinary teams can ensure that varying expertise contributes to the diagnostic process.
- Regular Case Reviews: Implementing routine case review meetings can help refine diagnostic accuracy through collective insights and continual learning.
In the domain of follicular lymphoma, recognizing the challenges in diagnosis ensures that practitioners remain vigilant and proactive, ultimately aiming for improved clinical outcomes.
Interdisciplinary Approach
In the realm of diagnosing follicular lymphoma, an interdisciplinary approach stands as a cornerstone, weaving a rich tapestry of expertise across various healthcare domains. This collaboration involves hematologists, pathologists, radiologists, and primary care physicians, all of whom bring their specialized knowledge to the table. Each professional has a distinctive lens through which they view patient care, and together they foster holistic assessments that enhance the diagnostic process.
The intersection of these varied specialties often results in more accurate and timely diagnoses. For instance, when a patient presents with suspicious symptoms, hematologists are adept in interpreting clinical signs and initiating necessary lab tests. Meanwhile, pathologists engage in examining biopsy samples, diligently identifying the lymphocyte characteristics that are pivotal in confirming follicular lymphoma. Radiologists add another layer by employing advanced imaging techniques, helping to map out the extent of disease progression. Such synergies are vital, especially in cases where the disease presents atypically or when overlapping symptoms complicate the clinical picture.
Benefits of an Interdisciplinary Team
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Each specialist contributes unique insights, reducing the risk of oversight.
- Improved Communication: Regular interactions facilitate better understanding of the patient’s condition, making sure everyone is on the same page.
- Streamlined Processes: Coordinated efforts lead to quicker decision-making and more efficient use of healthcare resources.
- Enhanced Outcomes: A united front not only speeds up diagnosis but can also lead to more tailored treatment plans.
The complexities involved in diagnosing follicular lymphoma exemplify the necessity of this collaborative approach. Diagnostic challenges can arise due to the subtle variances in lymphomas, with folicular lymphoma often masquerading in a manner that can lead to misdiagnosis if areas of expertise do not converge. Thus, ensuring that every voice is heard and considered in the diagnostic journey is crucial.
Considerations for Collaboration
An interdisciplinary strategy isn’t automatically flawless; it carries its own considerations. There may be moments of disagreement or varied interpretations of clinical data. In these instances, it's paramount to foster a culture of respect and open communication among healthcare providers to sidestep any tensions. Additionally, differences in scheduling and availability can pose barriers to regular collaboration.
In summary, the interdisciplinary approach underscores the collaborative spirit that is vital in navigating the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma. As we delve deeper, it becomes clear that uniting these diverse perspectives creates a fortified line of defense against the complexities of this disease.
Collaboration among Healthcare Professionals
The heart of any effective interdisciplinary approach lies in the collaboration among healthcare professionals. When asking why this aspect holds such significance, one must consider that diagnostic precision often bears a heavy reliance on collective expertise. Each professional walking into a case brings a slew of experiences and knowledge, paving the way for a thorough examination of each patient’s unique clinical presentation.
Collective case discussions can illuminate potential missteps that an individual might overlook. When a hematologist meets with a radiation oncologist to discuss imaging findings, new patterns may emerge that could redirect the diagnostic path. This heightened awareness can sometimes prevent the dreaded spiral of misdiagnosis that can plague patients.
Moreover, establishing rapport among team members can enhance workflow efficiency. With effective communication, professionals can share insights swiftly, thus avoiding the dreaded game of telephone where details might get lost or distorted.
Case Review Meetings
A pivotal component of this collaborative framework is the traditional case review meeting. During these gatherings, healthcare professionals along with their distinct skills come together to dissect challenging cases, share findings, and deliberate over the next steps in a patient’s diagnosis.
These meetings serve multiple purposes:
- Knowledge Sharing: Participants exchange knowledge about recent cases which might help in understanding patterns.
- Identifying Gaps: Reviewing cases enables the team to recognize gaps in understanding or diagnosis that can inform future practices.
- Innovative Strategies: Exposure to various perspectives often leads to brainstorming new strategies that can enhance diagnostic precision.
Nevertheless, accomplishing an efficient case review meeting requires a structured agenda to avoid aimless discussions. Each member must be encouraged to present their insights while remaining open to constructive criticism. This atmosphere nurtures a culture of learning that’s vital in continuously improving diagnostic approaches.
Conclusively, the interdisciplinary approach, bolstered by collaborative efforts and regular case review meetings, forms a bedrock for more accurate diagnosis of follicular lymphoma and enhances overall patient care.
Future Directions in Diagnostics
The landscape of diagnosing follicular lymphoma is in constant flux, fueled by technological advancements and a deeper understanding of molecular biology. The directions of future diagnostics hold significant promise, targeting precision and early detection. This topic is vital as it aims to enhance outcomes for patients through improved diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment strategies.
Emerging Technologies
Innovations in medical imaging and laboratory techniques are paving the way for breakthroughs in diagnosing follicular lymphoma. For instance, artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly becoming a cornerstone in the analytical processes. Algorithms can now assess imaging studies and histological slides more accurately than ever, providing quick information that helps in decision-making.
Another innovative approach is the use of liquid biopsy. Unlike traditional biopsies, which are invasive, a liquid biopsy involves analyzing a simple blood sample to detect genetic mutations or abnormal cells associated with lymphoma. This non-invasive method not only reduces patient discomfort but can also track disease progression or response to treatment over time:
- Convenience: Less invasive, leading to a better patient experience.
- Timeliness: Can provide quicker results compared to tissue biopsies.
- Monitoring: Allows for ongoing assessment of disease status.
As technology continues to evolve, developments in 3D imaging techniques also promise to enhance diagnostics. These technologies can provide detailed structural information of lymph nodes that traditional methods might miss, thus aiding in more accurate staging and assessment of disease spread.
Advancements in Genetic Research
The interplay between genetics and follicular lymphoma diagnosis continues to grow. Research in molecular genetics is uncovering potential biomarkers that could enable earlier diagnosis and more targeted therapies. Identifying specific gene mutations associated with follicular lymphoma can lead to tailored treatment plans that maximize efficacy and minimize side effects.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is particularly noteworthy in this domain. NGS can analyze vast amounts of genetic data simultaneously, facilitating the detection of complex genetic patterns. This capability vastly improves our ability to:
- Predict prognosis: Understanding genetic alterations can help in estimating disease behavior.
- Guide treatment decisions: Targeted therapies can be matched to specific genetic configurations.
- Identify novel therapeutic targets: Open doors for new drug development.
"With the rising currents of genetic research, the roadmap to better diagnosis of follicular lymphoma is becoming ever clearer. Not only does this offer hope for improved treatment protocols, but it also suggests a future where we can truly tailor healthcare to individual genetic profiles."
In summary, the future directions in diagnostics for follicular lymphoma are rich with possibilities that encourage a shift towards precise, patient-centered care. The integration of emerging technologies and advancements in genetic research both promise to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnoses, ultimately fostering a better understanding and management of the disease.







