Comprehensive Guide to Breast Hematoma Post-Surgery

Intro
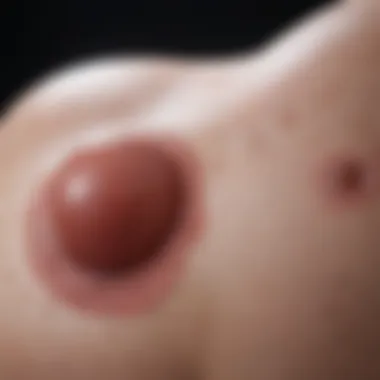
Breast hematoma can be a troublesome complication after various surgical procedures involving the breast. It’s important to understand this condition not just from a clinical perspective, but also from the patient’s viewpoint. The experience surrounding surgeries like breast augmentation, reduction, or mastectomy includes a host of expectations and concerns. When complications arise, such as hematomas, it can throw a wrench into the recovery process.
This guide aims to provide a deep-dive into the nature of breast hematomas, examining their definition, causes, symptoms, management, and implications on overall health and recovery. By shedding light on both medical and patient perspectives, healthcare professionals and those impacted by breast surgery can navigate the complexities of postoperative care with greater clarity and confidence.
Article Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Breast hematomas are blood collections outside of blood vessels that can develop after surgical interventions. They typically result from bleeding during or after surgery and may manifest through swelling, pain, and discoloration in the treated area. Understanding their onset, the risk factors, and the ways to manage them is crucial for ensuring optimal outcomes post-surgery.
Research Objectives
The objective of this article is multi-faceted. Primarily, we look to:
- Define what breast hematoma entails,
- Identify potential causes and risk factors,
- Describe symptoms that may arise,
- Explore management strategies including treatment options and preventive measures.
By addressing these components, we seek to equip both medical professionals and patients with essential knowledge to enhance recovery and minimize complications after breast surgery.
Key Results and Discussions
Main Findings
The occurrence of breast hematomas may not be as rare after surgical procedures, and certain factors can increase this likelihood. Age, body weight, and existing medical conditions such as clotting disorders can heighten risk. Necessary steps include rigorous postoperative monitoring and patient education regarding signs of hematoma development.
Implications of Findings
Understanding the intricacies of breast hematoma leads to improved patient outcomes. Recognizing the symptoms early and initiating prompt management can avert further issues and enhance the recovery trajectory. As medical professionals and patients engage in transparent discussions about potential risks, they can establish proactive strategies to mitigate complications.
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure" - Benjamin Franklin
This age-old adage holds true in the context of breast surgery as well, where awareness and education stand as the front line in preventing complications like hematomas. By following guidelines on postoperative care and maintaining open lines of communication, both providers and patients can ensure a smoother recovery process.
Intro
Breast hematoma is a topic that requires significant attention in the realm of breast surgery. Understanding this complication is crucial, not only for surgical success but also for ensuring better patient recovery and well-being. The process of undergoing breast surgery is multifaceted, and the aftermath can sometimes be complicated by conditions like hematomas. Therefore, it’s imperative for healthcare providers, patients, and their families to appreciate what this entails in terms of management and recovery.
Why This Matters
The consequences of breast hematoma can stretch far beyond the initial surgery. When blood collects in the breast tissue post-surgery, it can lead to pain, swelling, and sometimes even infection. This is not just a bump in the recovery road; it may necessitate further medical interventions, potentially delaying the healing process. Understanding the real-world implications means patients can be better prepared, while healthcare professionals can enhance their pre-and post-operative protocols. This knowledge can also help set realistic expectations regarding recovery timelines and outcomes,
Key Considerations in This Discussion
As we climb into the various aspects of breast hematoma, we will explore numerous significant elements, including:
- Definitions and Types: What exactly is a breast hematoma, and how do different surgical procedures play a role?
- Causative Factors: What can lead to the formation of these hematomas? Are there pre-existing conditions that patients should be aware of?
- Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing the signs early can make a world of difference; so how does one identify them?
- Management and Prevention: What are the best strategies for managing and preventing this condition?
By understanding these facets, a comprehensive picture of breast hematomas emerges, equipping all parties involved with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of surgery, recovery, and overall health.
Causes of Breast Hematomas
Understanding the causes of breast hematomas is pivotal in grasping how to mitigate risks associated with surgical interventions on the breast. Hematomas can occur due to various factors, making awareness essential for both healthcare professionals and patients. Recognizing the potential triggers can lead to improved surgical techniques, better preoperative evaluations, and ultimately, healthier outcomes.
Surgical Factors
Surgical factors play a significant role in the development of breast hematomas. The nature of the surgery itself, the technique employed, and even the experience of the surgeon can influence the likelihood of hematoma formation. Here are some of the key surgical elements most often involved:
- Type of Procedure: Certain surgeries, particularly those involving extensive tissue manipulation or removal, like mastectomy, inherently carry a higher risk of hematoma formation. The more invasive the procedure, the greater the potential for complications.
- Surgical Technique: Techniques that minimize trauma to the surrounding tissues, such as minimally invasive methods, are generally preferred. More aggressive methods can lead to excessive bleeding, resulting in hematoma.
- Intraoperative Management: Close attention during surgery to control bleeding and ensure proper closure of incisions can significantly reduce hematoma risk. For example, using precise suturing techniques and appropriate hemostatic agents can stabilize bleeding vessels.
- Duration of Surgery: Prolonged surgical times may increase complication risks, including hematomas. As time extends, so does the exposure of blood vessels, and healing mechanisms can be overwhelmed.
These factors underline the importance of meticulous surgical practice and underscore that attention to detail during operations can lead to a marked decrease in hematoma incidence.
Patient-Related Factors
On the flip side, patient-related factors also contribute significantly to the risk of developing breast hematomas post-surgery. It's crucial to consider the unique characteristics and health history of each patient. Some important factors include:


- Anatomical Considerations: Individual anatomical variations, such as breast tissue density, may influence how blood vessels are distributed and the likelihood of bleeding post-surgery.
- Coagulation Disorders: Patients with blood clotting disorders or those on anticoagulant medication face an increased risk for hematomas. Pre-existing conditions must be evaluated during the preoperative assessment.
- Age and Health Status: Generally, older patients or those with comorbid conditions such as diabetes or obesity may have delayed healing or increased vascularity, thereby heightening the risk of hematomas.
- Postoperative Care: Patient adherence to postoperative instructions, such as avoiding strenuous activities or movements that could stress the incisions, plays a vital role in preventing complications.
"Understanding both surgical and patient-related factors is paramount for reducing the risk of hematomas. Each element contributes to a broader picture that healthcare professionals must assess thoroughly."
In summation, acknowledging the causes of breast hematomas—both surgical and patient-related—is essential in navigating the complexities of breast surgery. This understanding fosters effective communication between patients and their healthcare providers and lays the groundwork for enhanced recovery strategies.
Symptoms of Breast Hematoma
The signs and implications of breast hematoma after surgery demand critical attention due to their impact on recovery and overall patient health. Recognizing these symptoms early can serve as a vital part of postoperative care, enhancing recovery and preventing complications. Awareness of symptoms not only helps healthcare providers monitor patients more effectively but also empowers patients to advocate for their own health. In this section, we break down the emergence of symptoms both immediately after surgery and their evolution over time, emphasizing the significance of each phase in management and care.
Initial Postoperative Signs
Immediately following breast surgery, patients may encounter a variety of initial signs that could signal the presence of a hematoma. These early symptoms are crucial as they often dictate the subsequent steps in management.
- Swelling: The most noticeable initial sign is often localized swelling around the surgical site. This swelling can vary in size and may become more pronounced over a few days.
- Bruising: Discoloration may appear in the form of bruising, which can manifest as dark purple areas on the skin surrounding the surgical incision.
- Pain and Tenderness: Many patients report increased pain or tenderness at the surgical site. This discomfort might be more intense than what was expected, often feeling different from standard postoperative pain.
- Temperature Changes: Some patients may experience warmth at the affected area. This could indicate blood pooling and may be of clinical relevance.
- Changes in Mobility: Difficulty moving the affected arm or side may occur, affecting daily activities.
It's important to note that while some swelling and bruising are typical after surgery, sudden increases in these symptoms, especially if they come with pain and other signs, should not be overlooked.
"Early recognition of changes in the surgical area can significantly improve management outcomes, making awareness crucial for both patients and healthcare providers."
Symptoms Over Time
As time progresses, the symptoms of a breast hematoma can evolve, influencing treatment strategies and patient care.
- Persistent Swelling: If swelling does not begin to subside after a few days, it may suggest the formation of a hematoma.
- Continued Bruising: Bruising can also change in color and intensity, often darkening before starting to resolve. If bruising continues to expand, it may indicate a larger hematoma.
- Increased Pain: While some pain is expected post-surgery, a notable increase after the initial recovery period can be a red flag.
- Fever or Chills: A systemic response such as fever can indicate infection or a significant shift in status; if present, it necessitates immediate medical attention.
- Feeling of Pressure: As the hematoma grows, patients might describe a sensation of pressure in the breast or surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort that could interfere with daily activities.
Understanding these evolving symptoms plays a critical role. Patients must be encouraged to communicate any concerning signs to their healthcare team promptly, ensuring timely intervention and fostering an environment of proactive care.
Diagnosis of Breast Hematoma
Diagnosing breast hematoma is crucial in managing postoperative complications effectively. The early identification of this condition can significantly influence recovery and the overall surgical outcome. If not diagnosed promptly, a hematoma can lead to complications such as infection or delayed healing, which can complicate the surgical process and prolong recovery times for patients.
An accurate diagnosis often involves a multi-faceted approach, combining both clinical examination and imaging techniques. This ensures that healthcare providers can differentiate between normal postoperative changes and significant complications, providing the necessary interventions when required. The benefits of thorough diagnosis lie in the ability to tailor treatment strategies, monitor progression, and mitigate associated risks.
Clinical Examination
A clinical examination stands as the first line of action when diagnosing breast hematoma. After surgery, surgeons or healthcare professionals typically assess the surgical site through a physical examination. They look for external signs like swelling, discoloration, or tenderness that could hint at the presence of a hematoma.
During the examination:
- Visual Inspections: Surgeons evaluate the area around the surgical site. Any unexpected swelling or bruising can be a red flag for potential hematoma formation.
- Palpation: By gently pressing on the breast tissue, clinicians can assess for fluctuations or tenderness that might indicate fluid buildup beneath the skin.
- Patient Reporting: Patients are encouraged to communicate any discomfort or unusual sensations they experience in the days following the surgery, which provides valuable context for the clinician.
Effectively, clinical examinations offer a firsthand opportunity to catch any irregularities early in the healing process, allowing for timely intervention if necessary.
Imaging Techniques
In addition to clinical evaluations, imaging techniques play a pivotal role in confirming a diagnosis of breast hematoma. They provide visual representations of the internal anatomy, helping clinicians identify any accumulating blood collections or fluid pockets that may not be detectable through a physical examination alone.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a widely used imaging modality in the diagnosis of breast hematoma. It utilizes sound waves to create real-time images of the breast tissue, allowing for the identification of fluid-filled areas. The non-invasive nature of this technique makes it a compelling choice for postoperative assessments.
Key Characteristics of Ultrasound:
- Accessibility: It's typically readily available in most clinical settings, making it an easy option for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Safety: There are no radiation concerns with ultrasound, making it suitable especially for patients who might need repeated assessments post-surgery.
A unique feature of ultrasound is its ability to differentiate between solid masses and fluid collections. It provides clear boundaries which let doctors assess the extent of the hematoma. However, one disadvantage is that it may not yield as detailed results compared to other imaging methods like MRI, specifically regarding tissue characteristics.
MRI
MRI offers another sophisticated approach to diagnosing breast hematoma. By utilizing magnetic fields and radio waves, MRI produces detailed cross-sectional images of the breast and surrounding structures. This method can be particularly beneficial for evaluating complex cases or when surgery complications are suspected.
Key Characteristics of MRI:
- High Resolution: MRI provides a comprehensive view of the breast tissue, allowing doctors to assess not just the hematoma but also any adjacent anatomical changes.
- Insight into Vascular Changes: MRI can delineate blood vessels and other critical structures, giving a fuller perspective of any potential issues that might arise.
The unique feature of MRI lies in its ability to offer insights into soft tissues, thus revealing deeper areas where hematomas may be hidden from surface exams. However, the downsides include higher costs, longer scan times, and the need for specialized equipment.


Management Strategies for Breast Hematomas
When dealing with breast hematomas, selecting an appropriate management strategy is crucial for ensuring optimal recovery. Breast hematomas can pose a significant challenge, not just in terms of physical complications, but also in their effects on emotional well-being. Understanding the various approaches available for managing this condition can empower both patients and healthcare providers in making informed decisions that ultimately contribute to a smoother healing process.
Conservative Management
Conservative management aims to utilize non-invasive methods that can facilitate recovery while minimizing additional risks. It focuses on monitoring the condition and applying simple interventions that are often sufficient in handling smaller hematomas.
Observation
A key element of observation is the careful monitoring of the hematoma over time. This approach often contributes positively to overall recovery by allowing the body to reabsorb the collected blood naturally. It is a widely accepted practice, especially for smaller hematomas where symptoms are not severe.
The main characteristic of observation is its non-invasive nature. It stands out as a beneficial choice because it avoids the potential complications associated with surgical interventions. By following a wait-and-see approach, clinicians can spare patients from unnecessary procedures, particularly when the hematoma shows no signs of significant growth or discomfort.
However, there are unique features to consider with this approach. While observation can often be effective, one must remain vigilant. If symptoms worsen or new signs emerge, this strategy might lead to delayed treatment. Thus, patients should be well-informed about what to watch for, empowering them to seek further evaluation when necessary.
Compression
Compression serves as another aspect of conservative management that can aid in minimizing hematoma size and discomfort. The use of a properly fitted compression garment can create gentle pressure on the area, helping to prevent further fluid accumulation.
This method is notable for its key characteristic of being both supportive and practical. Compression garments can be easily integrated into the patient's daily routine, making it a popular choice for those needing relief without invasive procedures. Their ability to stabilize the area promotes healing, which aligns perfectly with the goals of this article.
The unique feature of compression lies in its versatility. Adjustable garments can be tailored to fit various body types, enhancing comfort. However, there are potential disadvantages; excessive compression may lead to restricted blood flow or increased pain. Therefore, it is essential to find a balance and ensure that the garment is used correctly.
Surgical Intervention
In some cases, conservative management may not suffice, which leads to the necessity for surgical intervention. This option is important, particularly when the hematoma is large, symptomatic, or shows signs of infection. Surgical methods aim to remove the hematoma entirely or reduce its impact on the patient's health.
Drain Placement
Drain placement is a common surgical practice in managing breast hematomas. By facilitating the removal of accumulated blood through a drainage tube, this method allows for quicker symptom relief and healing. It can be particularly effective in cases where the hematoma is extensive or is causing significant discomfort.
The notable characteristic of drain placement is its proactive approach to treatment. Instead of waiting for the hematoma to resolve on its own, this method actively addresses the issue. Patients often experience considerable relief shortly after the procedure.
Still, consideration of unique features is critical. While drains can effectively alleviate symptoms, they also come with risks such as infection or complications at the site of insertion. Regular monitoring and proper handling of the drain are imperative to mitigate these risks.
Hematomectomy
Hematomectomy, the surgical removal of a hematoma, is employed when a large collection of blood is either causing severe discomfort or is suspected of creating additional health issues. It involves a more extensive procedure than drain placement and is often considered when other methods have not yielded satisfactory outcomes.
The key characteristic of this intervention is its decisiveness. Hematomectomy provides a thorough solution to eliminate a problem that could otherwise undermine recovery. For some patients, this may lead to an improved quality of life post-surgery, as it can clear potentially harmful complications away more rapidly.
However, as with any surgical option, there are advantages and disadvantages to hematomectomy. While it offers a solution to significant hematomas, it carries inherent risks like general anesthesia complications and recovery times that could be extended. Thus, discussions around this necessity should involve an in-depth conversation between patient and surgeon.
In summary, understanding the management strategies for breast hematomas is fundamental in guiding treatment decisions. Whether opting for conservative management or surgical intervention, recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of each approach helps in crafting a tailored recovery plan that addresses both physical and emotional needs.
Preventive Strategies
Preventive strategies play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of breast hematomas following surgical procedures. Understanding how to effectively reduce the chances of this complication can significantly enhance the recovery process and patient outcomes. By taking well-thought-out precautions before and during surgery, healthcare professionals can foster a safer environment, reducing not only the incidence of hematomas but also ensuring a smoother recovery for the patient.
Preoperative Assessment
A detailed preoperative assessment forms the backbone of any surgical intervention. This phase involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current medications, and overall health status.
Key components of a preoperative assessment include:
- Medical History Review: Understanding previous health issues, particularly those related to blood clotting or vascular health, is paramount. Conditions such as thrombocytopenia or anticoagulant therapy can increase the likelihood of hematoma formation.
- Physical Examination: A careful examination assesses the patient’s anatomical suitability for the planned procedure and identifies any potential risk factors that could complicate surgery.
- Patient Education: Informing the patient about the procedure itself and what to expect postoperatively can allay fears and ensure adherence to recovery protocols.
- Optimization of Health Conditions: Addressing any chronic conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, can improve surgical outcomes. Patients may need to wait until these conditions are stabilized before proceeding.
By thoroughly evaluating these aspects, the surgical team can tailor the approach to address specific risk factors, making it a step not to be overlooked.
Intraoperative Techniques
During the surgical procedure, various techniques can be implemented to minimize the risk of developing hematomas. These methods are designed to ensure not only the success of the surgery but also to reduce trauma to surrounding tissues.
Important intraoperative techniques include:
- Gentle Tissue Handling: Surgeons should aim to minimize tissue trauma by using precise techniques while handling breasts. Soft tissues should be respected, and any dissection should be done carefully to avoid unnecessary bleeding.
- Hemostasis: Strategies for achieving effective hemostasis during surgery are crucial. Utilizing methods such as electrocautery or harmonic scalpel ensures that blood vessels are sealed properly, reducing the risk of postoperative bleeding that could lead to a hematoma.
- Fluid Management: Adequate management of fluids during surgery prevents excessive fluid accumulation in tissues; it can sometimes complicate the surgical site. Balanced fluid intake aids in maintaining vascular stability and support healing.
- Drain Usage: In certain cases, the use of surgical drains can be invaluable in preventing hematoma formation. By providing an exit route for any accumulated fluid, drains can significantly decrease the pressure around the surgical site.


Effective intraoperative techniques can make a considerable difference in lowering the risk of breast hematomas, ultimately guiding patients to smoother recoveries and better health outcomes.
Incorporating these preventive strategies helps in formulating a robust plan against breast hematomas, enhancing both patient safety and surgical efficacy. Through a thoughtful approach that embraces both preoperative and intraoperative elements, healthcare professionals can significantly lessen the burden of this complication.
Impact on Recovery
The impact of breast hematoma on recovery cannot be overstated. Following breast surgery, the body undergoes a myriad of changes, and the presence of a hematoma can significantly alter recovery trajectories. Patients often find themselves navigating both physical and psychological hurdles, making it essential to understand how a hematoma can affect their overall healing process.
Physical Recovery
In the realm of physical recovery, the formation of a hematoma can present several challenges. When blood accumulates in the tissue, it can lead to increased swelling, pain, and discomfort. This might necessitate an adjustment in postoperative care. Patients may experience limitations in movement as their body tries to cope with the added pressure from the trapped blood.
Moreover, a hematoma might delay the natural healing process due to inflammation, extending the timeline for recovery more than what was anticipated. Complications can arise, sometimes even requiring surgical intervention to evacuate the hematoma. The presence of infection is also a concern; a hematoma can serve as a breeding ground for bacteria if not managed properly.
Factors influencing physical recovery include:
- Extent of hematoma: Larger hematomas may impact recovery more severely.
- Location: Hematomas located near nerves or incisions could pose additional discomfort.
- Therapeutic interventions: Appropriate management strategies can mitigate some adverse physical effects.
When a hematoma complicates recovery, clear communication between the patient and healthcare providers becomes critical. Adequate monitoring and assessments can help manage symptoms effectively, promoting a smoother recovery experience.
Psychological Impact
The psychological ramifications of developing a breast hematoma post-surgery can be profound yet is often overlooked. For many patients, surgery is a journey toward self-improvement, whether for cosmetic or medical reasons. When faced with unexpected complications like a hematoma, feelings of anxiety and concern can easily surface.
Patients might question their decisions, leading to self-doubt as they grapple with the emotional toll of seeing their recovery compromised. The uncertainty surrounding healing progress can heighten stress levels, impacting sleep quality and overall morale.
The support network plays a vital role here. Counseling and open discussions with family or support groups can help patients navigate the psychological landscape of their recovery. Learning coping mechanisms to deal with the added stresses can foster a sense of control in an otherwise uncertain time.
"The mental toll of recovery can be just as significant as the physical challenges, and it’s important to address both for holistic healing."
Key psychological aspects include:
- Anxiety about the healing process: Uncertainty can be mentally taxing.
- Impact of complications on body image: Patients may feel disheartened if their experience does not align with expectations.
- The role of social support: Engaging with loved ones and therapeutic professionals can ease distress.
In summary, the impact of a breast hematoma on recovery is a multifaceted issue that encompasses physical discomfort and psychological challenges. Addressing both facets—understanding the physical limitations it imposes and acknowledging the mental burden it creates—is key to successful postoperative outcomes.
Long-Term Considerations
The concept of long-term considerations after breast surgery is crucial to understanding the full scope of recovery and health implications related to breast hematomas. While many discussions often center on immediate postoperative recovery, it is the longer-term effects that may resonate more profoundly and shape the trajectory of recovery. Addressing these considerations not only aids healthcare professionals in managing ongoing care but also empowers patients to engage actively in their follow-up processes.
Recurrent Hematomas
Recurrent hematomas can present a significant concern for patients who have undergone breast surgery. These occurrences may arise due to various factors including underlying health conditions, surgical technique, or failure to properly manage the initial hematoma. For a patient, experiencing a hematoma more than once can be frustrating both physically and emotionally. It is paramount to remain vigilant.
- Monitoring is key: Patients should regularly check for any unusual swelling or changes in appearance at the surgical site. If anything seems amiss, it’s advisable to contact your healthcare provider without delay.
- A deeper understanding of one’s own health status can also play a role in preventing recurrence. For instance, those with blood clotting disorders should discuss their unique risks before and after surgery.
- Communication with healthcare providers: Establishing a good rapport with surgeons and medical staff can help in addressing any worries promptly. Valued input from patients plays a critical role in refining postoperative care.
Surgical Areas of Concern
Certain surgical areas may need heightened attention after hematoma formation. Every operation has its nuances, and the location of the surgery can affect healing processes differently. For example, surgeries closer to the chest wall might have a higher chance of complications than those further out.
- Tissue integrity: The way the tissue was handled and repaired plays into recovery. Surgeons should ensure that blood vessels are well cauterized to prevent excessive bleeding.
- Training and experience: As with many things, a surgeon's expertise and approach significantly influence long-term outcomes. Even though the best surgical techniques are implemented, outcomes can vary if a surgeon lacks experience in specific procedures.
- Scarring and tissue changes are also a consideration. These can influence not only cosmetic appearance but also how the breast feels over time. Many patients are pleasantly surprised when their concerns about appearance dwindle in importance, while awareness of sensation changes remains more prominent.
In summary, understanding the long-term considerations surrounding breast hematomas reinforces the necessity of ongoing evaluation and patient engagement. Being mindful of potential recurrent situations and maintaining open dialogue with medical experts can contribute to a smoother transition towards recovery. The road to health following breast surgery is often akin to a long game of chess - every move counts, and awareness can make all the difference in the outcome.
Ending
Understanding breast hematoma following surgical procedures is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This article highlights the significance of recognizing the complexities associated with this condition, from its formation to the potential effects on recovery. Not only does awareness contribute to better patient management, but it also fosters a collaborative environment between patients and their medical teams.
Summary of Key Points
Several key points emerge from our exploration:
- Definition and Formation: Breast hematomas usually occur when blood accumulates within the breast tissue post-surgery, potentially leading to complications.
- Symptoms to Watch: Initial signs such as swelling and discomfort can evolve into more severe issues if not monitored.
- Diagnosis Techniques: A combination of clinical examination and imaging, like ultrasound or MRI, is often employed to identify hematomas accurately.
- Management Options: Both conservative measures and surgical interventions exist, depending on the size and symptoms of the hematoma.
- Long-Term Impacts: Patients should be aware of the risks of recurrence and the specific surgical areas that may present higher chances of complications.
By synthesizing these elements, we arm ourselves with the necessary knowledge to navigate the complexities of breast hematomas, leading to effective and informed postoperative care.
Future Directions in Research
As the medical community continues to evolve, future research on breast hematomas could take several directions:
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: Improving non-invasive imaging could provide earlier detection methods, enhancing patient outcomes.
- Patient Education Programs: Developing comprehensive educational resources tailored to individuals undergoing breast surgery may promote better understanding and post-operative compliance.
- Longitudinal Studies: When researchers carry out extended studies, it can offer insights into the long-term effects, both physical and psychological, that arise from this complication.
- Minimally Invasive Approaches: Focusing on techniques that reduce hematoma risk during surgery may lead to fewer complications and quicker recovery for patients.
The journey into understanding breast hematoma does not end here but opens doors to further inquiry that may benefit both practitioners and patients in the years to come.







